You’ve built a beautiful website. The design is sleek, the images are crisp, and your products or services are ready for the world. But there is one major problem: nobody is visiting. It is a frustrating reality for many website owners—having a digital storefront that feels more like a ghost town.
Naturally, you start looking for solutions and stumble upon the concept of Search Engine Optimization. But then the doubt creeps in. Is this something you can handle, or do you need a computer science degree to figure it out?
Table of Contents
The answer to “Can I do SEO for my website myself?” is a resounding yes.
You do not need an expensive agency or a massive budget to start ranking on Google. You simply need a roadmap. This guide is designed to cut through the jargon and provide you with a clear path to DIY SEO success. By following these steps, you can start driving organic traffic to your site and building a sustainable digital presence completely on your own.
Understanding the Basics: Can I Really Do SEO Myself?
The reality of DIY SEO is that while it can be time-consuming, the fundamental concepts are logical and manageable. You are essentially trading “sweat equity” for money. Instead of paying a consultant thousands of dollars, you invest your time in learning and implementing the strategies.
To make this manageable, you need to understand the 80 20 rule of SEO. This is based on the Pareto Principle, which suggests that 80% of your results will come from just 20% of your actions. In the world of search engines, you don’t need to know every single one of Google’s 200+ ranking factors.

Instead, focusing on a few high-impact tasks—like creating great content and ensuring a solid technical foundation—will yield the majority of your results.
By mastering these SEO basics, you can drastically improve your website visibility without getting bogged down in technical minutiae.
Step 1: Technical SEO (The Foundation)
Before you write a single word of content, you must ensure your website is technically sound. Think of technical SEO as the foundation of a house; if it is cracked, nothing you build on top of it will stand.
Your first move should be setting up Google Search Console and Google Analytics. These free tools are non-negotiable. Search Console tells you how Google sees your site, alerting you to errors, while Analytics tracks who is visiting. Once those are active, you need to perform a basic technical SEO audit.
Two critical factors here are site speed and mobile-friendliness. Google uses “mobile-first indexing,” meaning it looks at the mobile version of your site to determine where you rank. Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights to check your loading times; if your site is slow, users will bounce, and your rankings will drop.
Finally, ensure you have an XML Sitemap submitted to Search Console. This acts as a roadmap, helping Google find and index your pages efficiently. Prioritizing mobile optimization and speed ensures you pass the initial “quality check” from search engines.
Step 2: Keyword Research (Finding What People Want)
You cannot optimize your site if you don’t know what your customers are typing into the search bar. Keyword research is the process of discovering these terms.
Start by brainstorming topics. Put yourself in your customer’s shoes. If you sell artisanal coffee, they aren’t just searching for “coffee.” They might be searching for “best brewing methods” or “light roast vs dark roast.” To validate these ideas, use tools like Ubersuggest, Ahrefs (free tools available), or Google Keyword Planner.
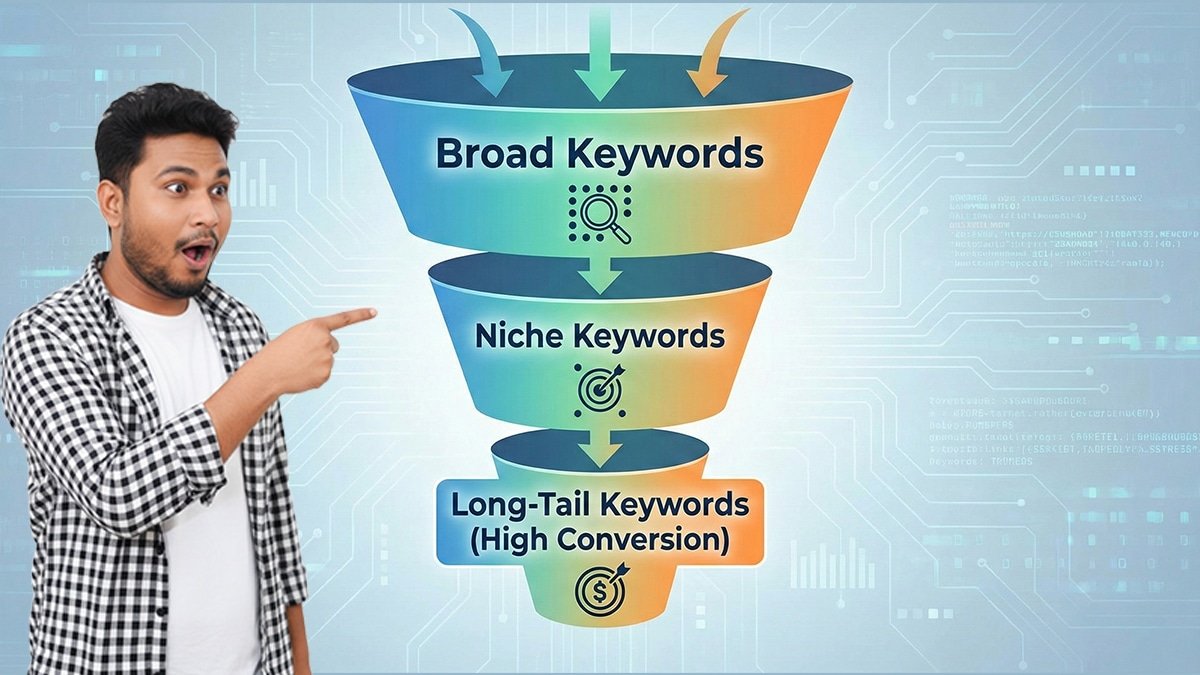
The secret sauce here is understanding search intent. Not all keywords are created equal. Some are informational (e.g., “how to brew coffee”), while others are transactional (e.g., “buy french press online”). For a new site, targeting specific long-tail keywords (phrases with 3+ words) is often easier than fighting for broad, competitive terms. These specific phrases usually indicate a user who knows exactly what they want.
Step 3: On-Page SEO (Optimizing Your Content)
Once you have your keywords, you need to place them where Google can find them. This is called on-page SEO.
It starts with your title tags and meta descriptions. These are the snippets that appear in search results. A compelling title and description can improve your Click-Through Rate (CTR), which is a ranking signal in itself. Within your content, use a proper heading structure. Your main title is the H1 (you should only have one per page), followed by H2s for main sections and H3s for subsections. This helps both readers and bots digest your content.
Don’t forget your visuals. Search engines cannot “see” images, so you must use content optimization techniques like adding descriptive Alt Text to every image. Ultimately, however, content is king. No amount of meta tags will save a poorly written article. Focus on creating high-value, comprehensive content that answers the user’s query better than anyone else.

Step 4: Off-Page SEO (Building Authority)
If On-Page SEO is what happens on your site, Off-Page SEO is what happens everywhere else. The most critical component here is backlinks.
So, how to get backlinks? Think of a backlink as a vote of confidence from another website. If a reputable site links to yours, it tells Google that you are a trusted resource, boosting your domain authority. You don’t need to spam forums to get these. Start with simple link-building strategies: write guest posts for other blogs in your niche, ensure your business is listed in local directories (citations), and share your content on social media.
While social media links don’t directly count as ranking signals, the off-page strategy of using social platforms drives traffic and brand visibility. The more eyes on your content, the higher the likelihood that someone will link to it organically.
How Much Does It Cost to SEO Your Website?
A common fear is that SEO will break the bank, but the cost varies wildly depending on how much work you are willing to do yourself.
If you choose the DIY route, the SEO cost is incredibly low, typically ranging from $0 to $100 per month. This budget covers your hosting and perhaps a subscription to a basic keyword tool, though many free alternatives exist. If you decide to hire a freelancer to help with specific tasks, you can expect to pay between $500 and $1,500 per month. For a full-service experience, hiring SEO agency services generally starts at $2,000 per month and can go much higher.

The verdict for most beginners asking “how do I run SEO on my website” is to start with the SEO budget friendly DIY approach. Validate your idea and get some traction before scaling up to paid professionals.
Common DIY SEO Mistakes to Avoid
As you begin this journey, be wary of common traps that can hurt your progress. The most common is keyword stuffing—jamming your target keyword into a sentence so many times it becomes unreadable.
This looks spammy to users and will get you penalized by Google.
Another mistake is ignoring User Experience (UX). You can have perfect keywords, but if your site is ugly, hard to navigate, or riddled with pop-ups, users will leave immediately. Finally, do not expect overnight results. SEO is a marathon, not a sprint. It often takes 3 to 6 months to see significant movement.
Conclusion
SEO doesn’t have to be a mystery. By following this roadmap—solidifying your Technical SEO, conducting proper Keyword Research, mastering On-Page content, and building Authority through links—you are well on your way to ranking.
Don’t let the scope of the work paralyze you. Start with just one page today. Optimize one title, fix one slow-loading image, or write one helpful blog post.
Explore Our Pages: Appsumo Deals, WP Themes, WP Plugins